Where has the implementation of the modern mobile app and patient engagement solutions fallen short?
Studies done in 2015 by Accenture and IMS have shown that the health system app development market was not meeting patient needs. In 2017, to follow up on these studies, Medical Web Experts analyzed the following leading health system’s mobile apps:
| Healthcare System | App Name | iOS | Android |
| Cleveland Clinic | Cleveland ClinicToday | ✓ | ✓ |
| Carolinas | Carolinas HealthCare System | ✓ | ✗ |
| Mayo Clinic | Mayo Clinic | ✓ | ✓ |
| Baptist Health South Florida | PineApp | ✓ | ✓ |
| Ascension | St. Vincents | ✓ | ✓ |
| Ascension | St. John | ✓ | ✓ |
| Tenet Health | Delray Medical Center | ✓ | ✗ |
| Tenet Health | Houston Northwest Medical Center | ✓ | ✗ |
| Trinity Health | Trinity Health | ✓ | ✓ |
| Kaiser Permanente Health Foundation | Kaiser Permanente | ✓ | ✓ |
| Dignity Health | My Care Dignity Health | ✓ | ✓ |
| NewYork-Presbyterian Healthcare System | NYP | ✓ | ✓ |
| Adventist Health System | Adventist Midwest Health Connect | ✓ | ✗ |
| Spectrum Health | My Health | ✓ | ✓ |
| Sutter Health | Sutter Health San Carlos | ✓ | ✓ |
| Sutter Health | My Health | ✓ | ✓ |
| Covenant Health | Virtual Care | ✓ | ✗ |
| Intermountain Healthcare | Health Hub | ✓ | ✓ |
| Sentara | Sentara | ✓ | ✓ |
| CHI Franciscan | CHI Franciscan | ✓ | ✓ |
| Legacy Health | Legacy Health | ✓ | ✓ |
| Novant Health | Novant Health | ✓ | ✓ |
Table 1: List of mobile apps from top health systems used for analysis and the operating system(s)on which they are available.
The results of this analysis show that while most large health systems have mobile apps, they continue to fail to provide value to patients in several important ways, including:
- Mobile app features have limited functionality
- App stores have misleading functionality descriptions
- Core features are not aligned with those most requested by patients
- Health systems lack focus on a single app
- Apps have limited downloads and/or poor ratings
One of the ways in which Medical Web Experts assessed the data gathered was to score the apps in terms of the quality of the user experience and the level of difficulty in implementing the features and functionalities provided. The following graph shows how the apps analyzed score along these two dimensions:
Image 1: Ranking of mobile app functionalities among top health systems based on user-experience and level of difficulty in implementation.
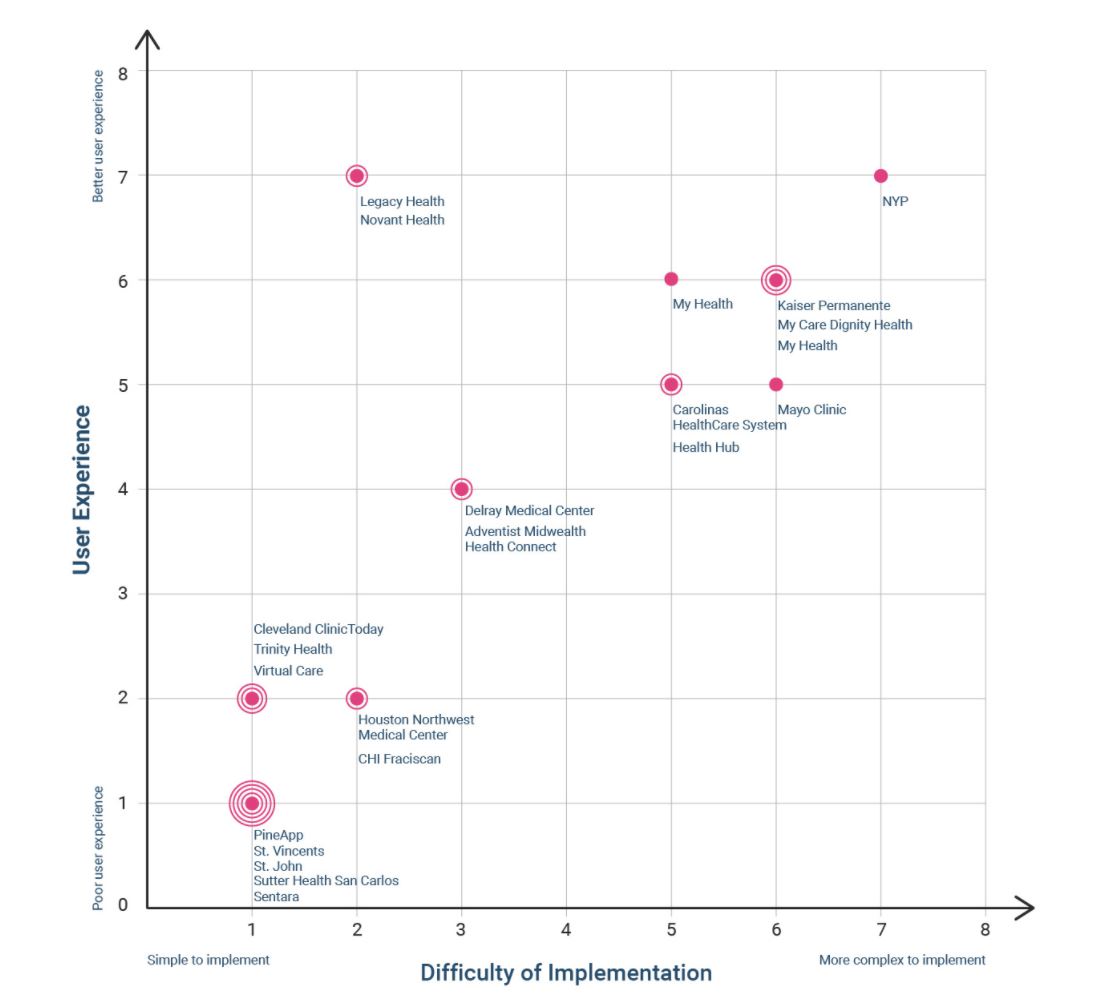
To much surprise, Medical Web Experts saw that almost 50% of the apps evaluated are clustered in the portion of the graph representing easy to implement apps with poor-user experience features. While not every health system and app evaluated fell into this area of the graph, it is concerning that such a large portion of the applications are valuing ease of implementation over user experience.
To make matters worse, often times the descriptions within the app stores are misleading. For example, many features simply launch the App Store or Google Play store and require the patient to download additional apps. This is a problem as in a single health system, a patient might be expected to download up up to 5 apps, each one offer a specific feature. App descriptions make no mention of these additional download requirements and promote such features as if they were part of the app itself. This disconnect between the user expectation and the actual delivery of the features in the app leads to a poor brand experience, deletion of the app and disillusioned patients.
Perhaps most disappointing is that of the the features most frequently requested by patients, according to the 2015 studies, are still woefully absent or implemented with the minimal amount of effort possible. The features in question are:
- Electronic medical records access
- Appointment scheduling and changes
- Prescription refills
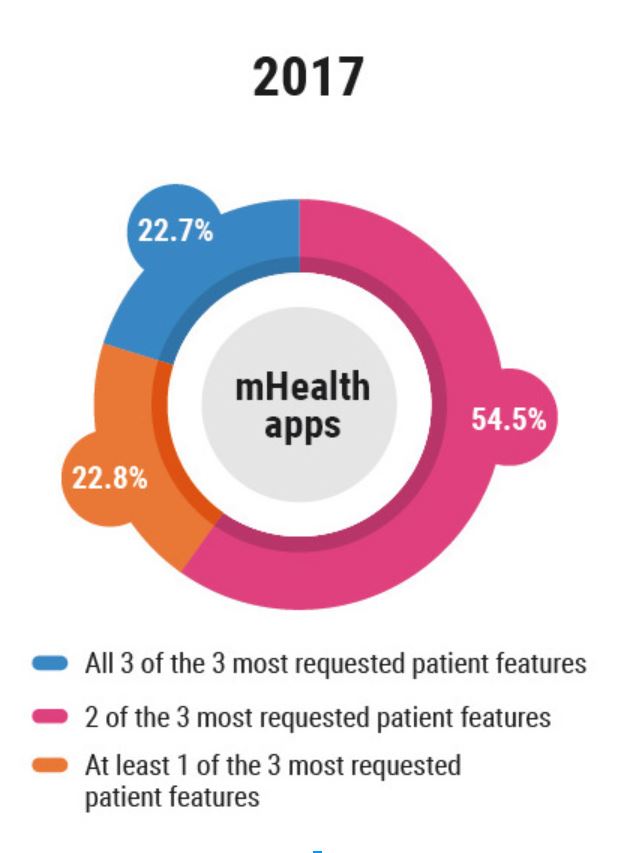
More precisely, two years after the initial 2015 studies were released, only 22.7% of the mobile apps evaluated contained all three of these features. The below pie chart shows the current day breakdown of key features offered by mobile apps; while it is an improvement, the healthcare mobile app development industry still has a long road ahead.
Image 2: Percentage of top health system mobile apps in 2017 that provide at least one of the 3 most requested patient features as defined in Accenture’s 2015 report.
So, why is healthcare mobile app development falling short? There are many reasons, including lack of resources, conflicts in internal politics, and complications in implementation. However, the founder of Medical Web Experts, John Deutsch, believes that “the overarching issue is that healthcare systems are not seeing the direct connection between a high-functioning mobile app and better patient engagement, which is proven to improve outcomes and reduce bad debt.” As reported by Accenture in 2015, large healthcare systems and networks that provide an innovative digital patient engagement platform could save as much as $100 Million per year per hospital in avoided revenue loss.
Moving forward, healthcare system app development will need to focus on patient engagement through superior mobile apps that provide the functionalities patients want with the user experience they have come to expect. Effectively accomplishing these goals will result in increased brand loyalty.
This article is brought to you by Medical Web Experts, a leading provider of custom web development and marketing solutions for the healthcare industry, meeting the sector’s the increasing demand for HIPAA-compliant technology and digital patient services. Medical Web Experts creatively helps clients to gain competitive edge by leveraging the latest technologies to improve efficiency, enhance their web presence, and heighten patient engagement.

